Poisson is the simplest traffic model and is used to work out how many lines are required if the traffic figure (in Erlang) during the busiest hour is known. The Poisson distribution is based on the following assumptions:
- Calls are served in random order.
- There are an infinite number of sources.
- Blocked calls are held.
- Holding time is exponential or constant.
The usage of Poisson in ForecastX™ is similar to ErlangB. See below for information on ErlangB.
To use the Poisson forecasting technique:
- Click on the Forecast Method tab.
- In the Forecast Technique area, scroll through the list of methods and select Poisson. The Poisson Forecasting technique displays.
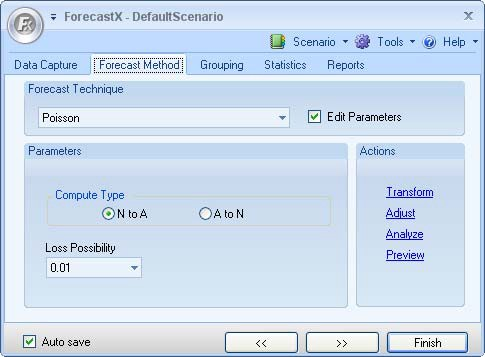
- Select Edit parameters to activate Poisson’s parameters.
- In the Compute Type area, select either N to A, or A to N.
- In the Lost Possibility area, select one of the options for the percentage of loss that is possible.
- Click Finish.