Erlang C assumes that all blocked calls stay in the system until they can be handled. This model can be applied to the design of call center staffing arrangements where, if calls cannot be immediately answered, they enter a queue. The Erlang C distribution is based on the following assumptions:
- Calls are served in order of arrival
- There are infinite number of sources
- Blocked calls are delayed
- Holding times are exponential
To use the Erlang C forecasting method:
- Click on
 and open the ForecastX_Erlang.xls file.
and open the ForecastX_Erlang.xls file.
Note: The ForecastX_Erlang.xls file is a data example to demonstrate how the Erlang C method is used. For your company’s purposes, you will have your own data available. - Click on the Erlang C1 ile.
- Click in a cell containing data and open ForecastX by clicking on
 . ForecastX displays with the Data Capture tab open.
. ForecastX displays with the Data Capture tab open.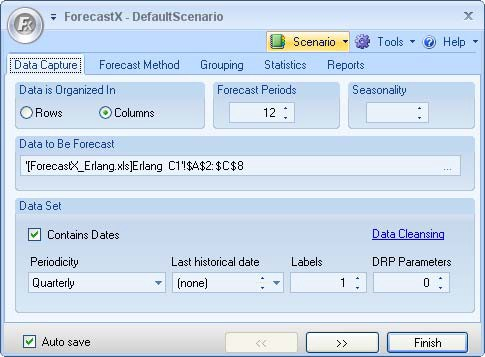
- In the Forecast periods area, type in 4 to forecast for the next four quarters.
- Click on the Forecast Method tab.
- In the Forecast Technique area, scroll through the list of methods and select Erlang C.
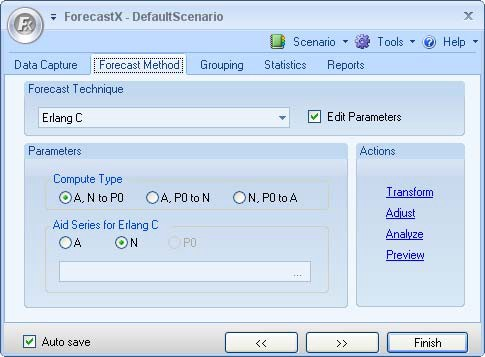
- Select Edit parameters to activate Erlang C’s parameters.
- In the Compute Type area, select one of the following options:
- A, N to PO
- A, PO to N
- N, PO to A
- Note: N is the number of servers, P0 is the probability of delay greater than zero, and A is traffic, measured by Erlang.
- In the Aid Series for Erlang C area, select one of the options.
- Click on the textbox. The Wizard dialog displays.
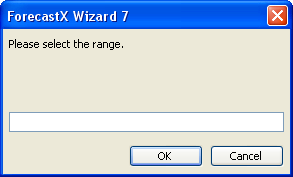
- Highlight the Probability of Delay column in the Excel spreadsheet and click OK.
- Click Finish.
As you review the results within the Standard Report, notice how ForecastX created the forecast for the number of servers for the next 4 periods and calculated the traffic based on the probability of delay.